Published on May 2021 | Public Health
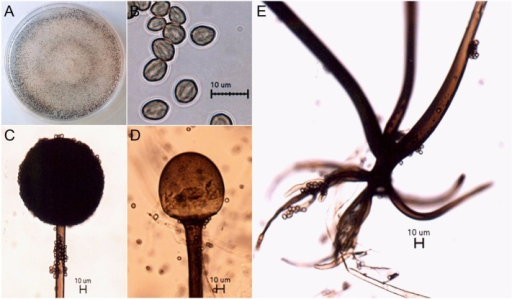
Abstract This time last year in May 2020 India was under lockdown phase, many theories invented and discovered without any scientific evidence about India’s surprisingly low rates of Sars-CoV-2 infection, included variety of factors such as hot weather, natural immunity, heard immunity, robust health system, highly qualified doctors, natural healers and the India’s big proportion of young healthy people; as well as also due to the complete lockdown . India was doing so well that in biggest cities like Mumbai and Delhi, officials had begun dismantling temporary COVID-19 facilities. Comparing it to current scenario in May 2021, covid-19 & Mucormycosis (new epidemic ¬ifiable disease declared by several states of India) cases and deaths are a big problem faced by healthcare department and system of India. There are chances of emergence of other diseases which can become epidemic in India due to several factors like improper techniques applied for disposing dead bodies of covid-19 patients etc in rivers low burials to be digged by animals and improper immunization and care of pregnant women. The shortage of medicine for treatment of Mucormycosis is so acute that people are dying daily waiting to get medicine and proper treatment at hospitals. Daily rates of covid-19 cases are currently about 200,000, but now the main concern in India is Mucormycosis death rate. Several theories are again being invented and discovered on daily basis coming through news media and other channels again misguiding peoples and creating panic. It seems that the Indian scientific bodies are not able to understand and formulate a proper protocol for treatment and management of pandemic and epidemic. Cases of Mucormycosis called as black fungus(improper terminology) in layman language by some people in India, a potentially serious condition that causes blurred or defective vision, severe chest pain and little or severe breathing difficulties, have increased in India, mostly among COVID-19 patients. More than 8,848 cases of Mucormycosis have been found across the various states of India as of May 21, according to the govt . The covid-19 pandemic have not subsided yet in India from which the healthcare system is struggling since2020 January .Mucormycosis represents a group of life-threatening infections caused by fungi of the order Mucorales which are difficult-to-manage owing to limited as well as less number of diagnostic tools and therapeutic options available till date particularly in developing countries like India having a large portion of population dwelling in villages with poor infrastructure and limited resources in healthcare (both private and public). Fungi of order Mucorales divided into six families, all of which have capacity to cause Mucormycosis. Rhizopus oryzae is the most common cause of infection usually. Others are Rhizopus microspores, Rhizomucor pucillus, Mycoclaudus corymbifier, Apophysomyces elegans, etc. Reclassification have abolished class zygomycetes and placed the order Mucorales in the subphylum Mucoromycotina. Mucormycosis is very invasive and progressive disease with greater than 40% morbidity and mortalities. For diagnosis a very high index of suspicion and history of patient is necessary to initiate early therapy to achieve better outcome. I review here advances in pathological understanding, modern diagnostic tools including computed tomography (CT), and serum polymerase chain reaction and therapeutic options with different available medicines. Keywords Mucormycosis, fungal, patient, treatment, covid-19 Reverse Halo sign, PCR, Isavuconazole, Liposomal amphotericin B,